Published on 09 Oct 2025
Tax rate changes in Australia directly impact your business cash flow, requiring immediate attention to manage liquidity, avoid compliance penalties, and maintain operational stability. With the Australian Taxation Office (ATO) increasing enforcement and multiple rate adjustments taking effect throughout 2025, understanding these changes has never been more critical for your financial planning.
How Tax Rate Changes Create Cash Flow Challenges
Recent tax adjustments affect everything from company tax rates and superannuation guarantee contributions to Pay As You Go (PAYG) instalments and Goods and Services Tax (GST) obligations. These changes create both opportunities to reduce tax liabilities and challenges that can strain your working capital if not managed properly.
The most significant challenge lies in the timing mismatch between earning income and paying the corresponding tax obligations. Unlike other business expenses that align with revenue generation, tax payments often occur months after the income is earned, creating potential cash flow gaps that can disrupt operations.
Are your tax payments straining business cash flow?
Schedule a complimentary consultation with us today to help smooth tax timing and reduce cash flow gaps.
The Compound Effect of Multiple Tax Changes
Australian businesses currently face several concurrent tax changes that amplify cash flow pressure. The company tax rate remains at 25% for Base Rate Entity (BRE) eligible businesses and 30% for all other companies, but eligibility criteria continue to affect which rate applies to your business. Companies must have aggregated turnover below $50 million and no more than 80% passive income to qualify for the lower company tax rate.
For sole trader businesses, individual income tax rates apply to taxable income. Australian residents pay tax on their total assessable income, which includes business profits, salary from employment, and other income sources. The Medicare Levy of 2% applies to most taxpayers, with additional Medicare Levy Surcharge potentially affecting higher income earners.
The Superannuation Guarantee (SG) rate increased from 11.5% to 12% on 1 July 2025, representing the final scheduled increase in this series. This change applies to all salary and wages paid from 1 July onwards, even if the pay period started before this date, creating immediate cash flow implications for payroll management.
PAYG Instalment Adjustments and Cash Flow Impact
Pay As You Go (PAYG) instalments help spread tax payments throughout the year, but rate changes and calculation adjustments can create unexpected cash flow requirements. The ATO uses predetermined amounts or instalment rates calculated on your business and investment income to determine how much tax you need to pay in advance.
Business owners can choose between predetermined amounts calculated by the ATO or applying an instalment rate to their business and investment income. Companies with business and investment income over $2 million that aren’t small or medium business entities cannot use predetermined amounts, forcing them into the potentially more volatile rate-based calculations.
Many taxpayers find that PAYG instalments don’t align perfectly with their actual tax liability, particularly when income fluctuates throughout the financial year. This misalignment can create cash flow challenges when the correct amount of tax differs significantly from instalment payments made.
GST Cash Flow Timing Challenges
Goods and Services Tax (GST) create unique cash flow challenges because you collect GST from customers but may not pay it to the ATO immediately. Small businesses with aggregated turnover under $10 million can choose cash accounting, which aligns GST payments with actual cash receipts and helps manage cash flow more effectively.
The choice between cash and accrual accounting for GST significantly affects cash flow timing. Under cash accounting, you only pay GST when you receive payment from customers, providing natural cash flow alignment. However, this method may not suit all business models, particularly those with extended payment terms or significant credit sales.
When you lodge your Business Activity Statement (BAS), you’ll either owe money to the ATO or be entitled to a refund. The timing of these payments affects your cash flow, particularly for businesses with seasonal variations or irregular income patterns.
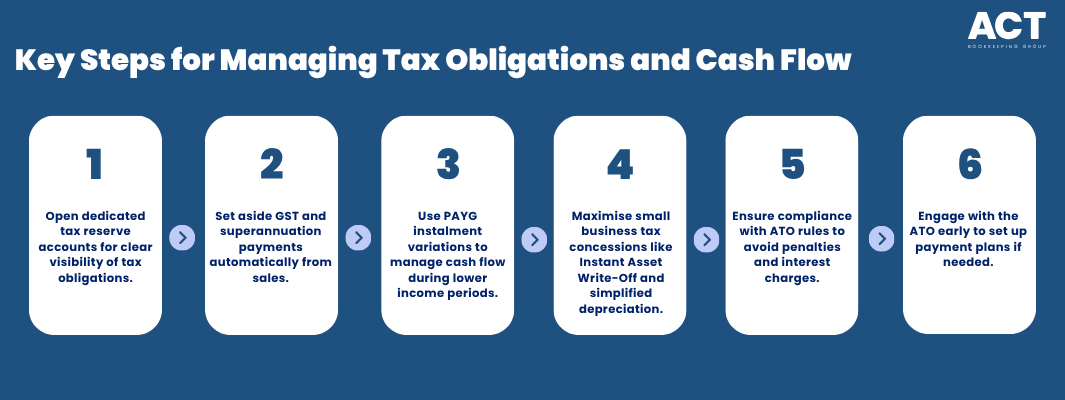
Strategies to Manage Tax Obligations and Protect Cash Flow
Effective tax cash flow management requires proactive planning that anticipates obligations before they become due. The key lies in creating systems that automatically set aside funds for tax payments while maintaining sufficient working capital for daily operations.
Establish Dedicated Tax Reserve Accounts
Opening separate bank accounts specifically for tax obligations provides the foundation for effective cash flow management. This strategy prevents accidental spending of money earmarked for tax payments and creates clear visibility of your tax position at any time.
For GST obligations, set aside the correct amount from each sale that includes GST. This ensures you always have sufficient funds when quarterly Business Activity Statements become due. The amount you need to withhold depends on your business model and whether you’re eligible for certain deductions.
Superannuation obligations require a separate reserve equal to 12% of eligible employee earnings. With the rate increase from 11.5% to 12%, businesses need to adjust their automatic transfers to reflect the higher obligation. For a business with a $500,000 annual payroll, this represents an additional $2,500 per year that must be factored into cash flow planning.
Utilise PAYG Instalment Management
PAYG instalment variations provide powerful cash flow management tools when used strategically. If your business income decreases or you expect lower profits, you can vary your instalments downward to preserve cash flow. However, ensure variations reflect realistic expectations to avoid penalties and interest charges.
The ATO website provides tools to help determine appropriate variation amounts based on current year projections. These calculators consider your estimated instalment income and calculate the tax liability, providing a basis for informed cash flow decisions.
When you lodge your tax return at the end of the financial year, any excess PAYG instalments paid will be refunded, while shortfalls create additional tax payable. Planning for these potential variations helps maintain stable cash flow throughout the year.

Maximise Small Business Tax Concessions
Small business entities with aggregated turnover under certain thresholds can access numerous concessions that improve cash flow outcomes. The Instant Asset Write-Off allows eligible businesses to claim immediate deductions for assets, reducing the amount of tax payable in the current financial year.
Strategic timing of asset purchases can create significant cash flow benefits. Purchasing eligible assets before 30 June allows you to claim deductions in the current year, reducing tax liabilities and improving cash flow. However, ensure assets are installed and ready for use by year-end to qualify for the deduction.
Simplified depreciation rules allow eligible businesses to write off assets faster than standard depreciation schedules. This accelerated approach to claiming the cost of business assets improves cash flow by reducing tax obligations sooner.
Plan for ATO Compliance and Penalty Avoidance
The ATO has resumed more aggressive enforcement of tax debts, making compliance planning essential for cash flow protection. Interest charges on overdue tax debts make late payments extremely expensive, while penalties for non-compliance can significantly impact your business finances.
Director Penalty Notices and garnishee actions have resumed, creating personal liability risks for company directors when superannuation or PAYG withholding obligations remain unpaid. This enforcement shift makes proactive cash flow management critical for business sustainability.
Engage with the ATO early if cash flow challenges threaten your ability to meet tax obligations on time. The ATO offers payment plans and other arrangements for businesses that demonstrate genuine commitment to managing their tax affairs responsibly.
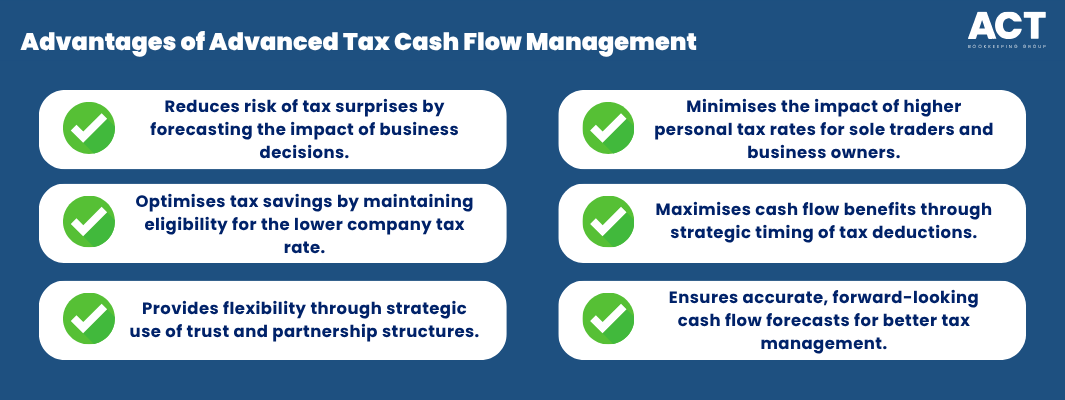
Advanced Cash Flow Planning for Tax Obligations
Sophisticated cash flow management goes beyond simply setting aside money for known obligations. It involves forecasting tax impacts of business decisions, optimising timing of income and expenses, and creating contingency plans for unexpected tax liabilities.
Integrate Tax Planning with Business Strategy
Company structure decisions significantly impact both tax rates and cash flow patterns. Businesses approaching the $50 million aggregated turnover threshold need to plan for the potential increase from 25% to 30% company tax rate if they lose Base Rate Entity status.
For companies eligible for the lower company tax rate, maintaining this status becomes crucial for cash flow management. The reduced rate applies to the first $50 million of taxable income, providing substantial savings that can be reinvested in business growth or maintained as cash reserves.
Trust and partnership structures can provide cash flow flexibility through different distribution strategies. However, ensure these structures comply with all relevant tax laws and serve genuine business purposes rather than attempting to avoid legitimate tax obligations.
We’re more than bookkeeping experts
As part of ACT Tax Group, we offer complete accounting and business advisory services tailored to your needs.
Monitor Individual Tax Obligations
Business owners operating as sole traders need to consider how business profits affect their individual tax position. Business income adds to other income sources when calculating total taxable income, potentially pushing taxpayers into higher tax brackets.
The Medicare Levy and potential Medicare Levy Surcharge apply to total taxable income, including business profits. Higher income earners may also face additional tax obligations that need to be factored into cash flow planning.
Charitable donations and other tax deductions can help reduce taxable income, but timing these deductions strategically maximises their cash flow benefits. Consider bunching deductible expenses into specific financial years to optimise your tax position.
Implement Robust Forecasting Systems
Effective tax cash flow management requires accurate forecasting that considers seasonal business patterns, timing of major transactions, and interaction between different tax obligations. Modern accounting software can automate many calculations, but businesses need systems that provide forward-looking insights rather than just historical reporting.
Monthly cash flow forecasts should include all tax obligations, considering their different timing cycles. GST and PAYG withholding are typically quarterly, while income tax instalments follow predetermined schedules. Superannuation guarantee payments have specific due dates that vary based on payment frequency.
For businesses with employees, factor in the cost of additional compliance obligations. Employers must withhold tax from employee salaries and pay this to the ATO regularly. The amount to withhold depends on each employee’s earnings and their tax-free threshold eligibility.
Conclusion
Tax rate changes represent both challenges and opportunities for your business cash flow management. The key to success lies in proactive planning that treats tax obligations as integral components of your financial strategy rather than unavoidable burdens.
Recent changes including the 12% superannuation guarantee rate, ongoing company tax rate structures, and evolving PAYG and GST requirements create complexity that demands systematic management. However, businesses that understand these obligations and plan accordingly can maintain healthy cash flow while optimising their tax positions.
Take action now to review your current tax cash flow management systems. Establish dedicated reserve accounts, update your forecasting to reflect current rates, and ensure your payroll systems accommodate the new superannuation guarantee rate. Consider engaging professional advice to understand the complexity and ensure compliance while protecting your business’s financial health.

